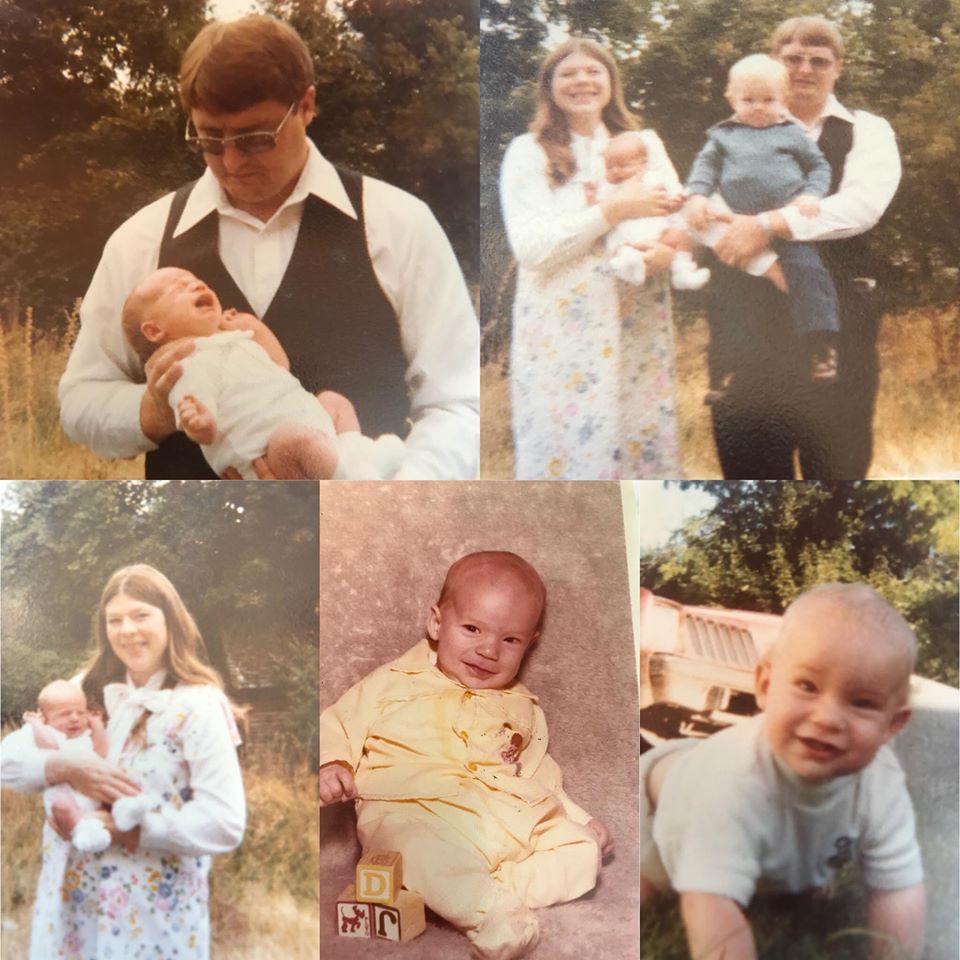
My Take Tuesday: Thanksgiving Dinner in Emery, Utah
The sense of smell is closely linked with memory, probably more so than any of our other senses. Those with full olfactory function may be able to think of smells that evoke particular memories; for me, the smell of turkey in the oven takes me back to Thanksgivings of long ago. As this homeward journey begins, I find myself seated at a table in my grandparents house in Emery, UT.
Grandma makes the best food! The fresh baked rolls, the stuffing, the potatoes, roasted butternut squash – each dish renders a unique and enticing smell. With the ever-more ready turkey roasting in the oven, these combine, creating a signature fragrance greeting guests the moment they step through the front door. We salivate as we anxiously await the assortment of generations of family recipes cooked to perfection.
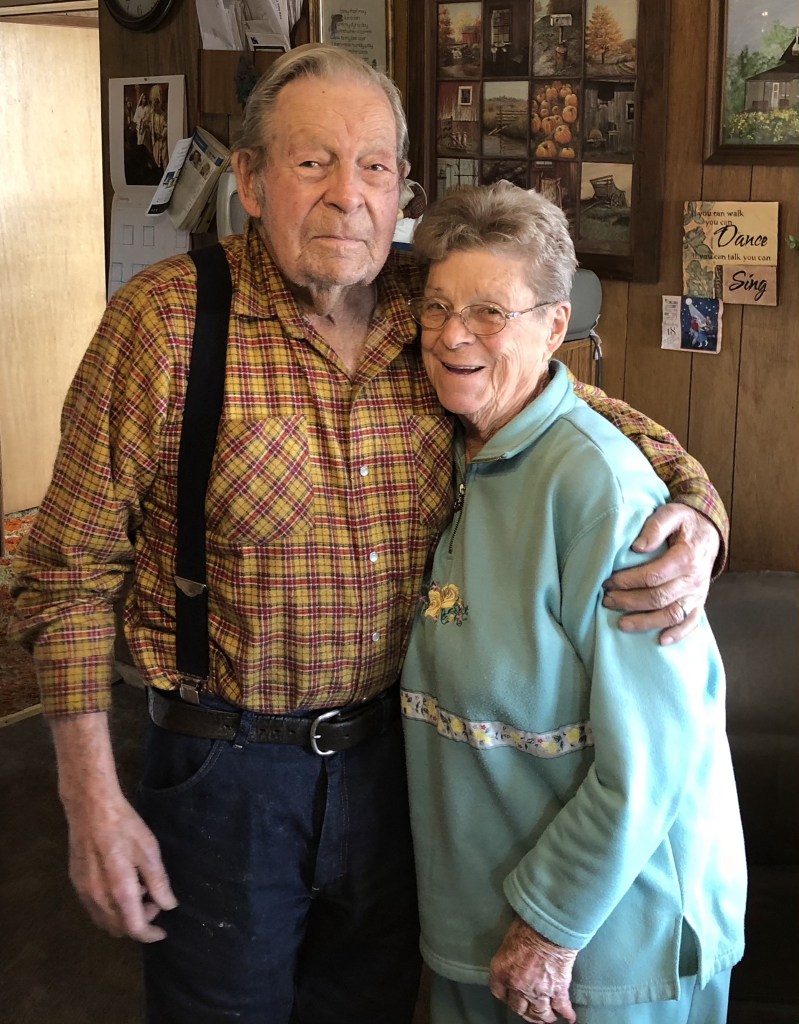
I remember exactly where I sat at the table, facing south, sitting across from my siblings and cousins. The sounds of the adults in the kitchen enjoying a home cooked meal as the delectable smells, good conversation, and the comfortable atmosphere make me feel at peace. As I close my eyes, I readily am able to conjure a significant mental image of Thanksgiving dinners at the home of Hugh and Shonna Peterson.
The joyous bustle and the incessant hum of conversation combine to create a warm atmosphere. The stokermatic furnace in the living room, with its gentle smell of burning coal, adds to the homey ambiance. As we reminisce and laugh, we give our diets a hall pass, stuffing ourselves in a way we would never dream of the other 364 days of the year. But more than the food we savor, it is the scent of the feast that we love and the constancy of family that makes us so complete.
After eating, I usually end up sitting with my cousins around the TV, watching a football game or laughing hysterically at the Farley Family Reunion VHS.
Later on, I return to the warm glow of the kitchen, Just in time to hear my grandpa telling a story from his younger days. I have never met anyone that can tell a story like Hugh Peterson. His excellent memory weaves a tapestry of nostalgia. With each word we move closer to the edge of our seats. With a smile on his face, and just a tad of embellishment, he tells a story like a boss. He makes us all literally laugh until we cry.
I will forever cherish these memories and conversations around the dinner table in Emery, Utah. They will forever remain a refreshing change from the chaos of everyday life. I will always remember the Peterson Family Thanksgivings as one of my most precious memories.
Since yesterdays are gone, and tomorrows are never promised, lets make this Thanksgiving count. Spend time with family and friends. Let us love and laugh and live in the moment. Be sure to spend time with the people in your life who want you to be in theirs. Cherish the people in your life who accept you for who you are, support you in the things you chose to do and, no matter what, are there for you.
And that is my take.
N. Isaac Bott, DVM